Dermatology is the medical science that addresses conditions of the skin, hair, and nails. We take a comprehensive approach to treating a variety of conditions, from acne and rosacea to hair loss and skin cancer. Our goal is to help each patient achieve healthy, beautiful skin through surveillance, diagnosis, treatment and proper skin care.
Hair and nails are a natural extension of the skin and play an essential role in protecting the body from external factors in the environment. Being aware of any drastic changes to either the hair or nails is extremely important because it can be an indicator that something else is going on in the body. Often, patients do not realize that dermatologists also treat hair and nails. In fact, the examination of the hair and nails is part of a complete skin exam.



The most common dermatologic conditions we evaluate and treat include, but NOT limited to:
These pesky brown or gray spots known as solar lentigines aren’t really caused by aging, though they do become more common as you get older. You get them from exposure to sunlight, which is why they tend to appear on your face, hands, and arms.
Alopecia is a condition that causes a person’s hair to fall out. It is an autoimmune disease; that is, the person’s immune system attacks their own body. In this case, their hair follicles. When this happens, the person’s hair begins to fall out, often in clumps the size and shape of a quarter. The extent of the hair loss varies; in some cases, it is only in a few spots. In others, the hair loss can be greater. There is no cure for alopecia. But hair often re-grows on its own and treatments such as steroids, oral and topical medications can help the hair re-grow more quickly. See our treatment options here.
A boil (abscess) is a skin infection that starts in a hair follicle or oil gland. At first, the skin turns red in the area of the infection, and a tender lump develops. After four to seven days, the lump starts turning white as pus collects under the skin. The most common places for boils to appear are on the face, neck, armpits, shoulders, and buttocks. When one forms on the eyelid, it is called a sty (chalazion). If several boils appear in a group, this is a more serious type of infection called a carbuncle.
The herpes simplex virus causes small, painful, fluid-filled blisters on your mouth or nose. Cold sores last about 10 days and easily spread from person to person. Triggers include fever, too much sun, stress, and hormonal changes like periods. You can treat cold sores with antiviral pills or creams.
Dandruff or Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin condition that it is characterized by a red and scaly, flaky scalp. It occurs most commonly in infants, middle-aged adults and seniors, particularly in those who have oily skin or hair. Seborrheic dermatitis also occurs in some patients with diseases of the immune or nervous systems. While there is no cure for this chronic condition, seborrheic dermatitis can usually be controlled by medicated shampoos or topical creams. If your dermatologist makes a diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis, he or she may recommend that you try these treatment options to treat the symptoms that accompany the disorder.
Eczema is a blanket term for several non-contagious conditions that cause inflamed, red, dry, and itchy skin. Doctors aren’t sure what makes eczema start in the first place, but they do know that stress, irritants (like soaps), allergens, and climate can trigger flares. In adults, it often appears on the elbows, hands, and in skin folds. Several medications treat eczema. Some are spread over the skin, and others are taken by mouth or as a shot. There is no cure for eczema, but, in most cases, it is manageable through treatments like oral medications, steroid creams and light therapy.
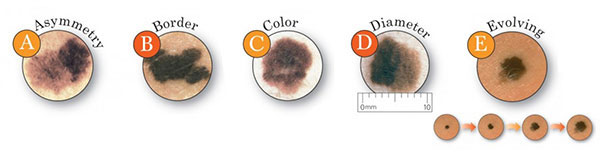
Nail fungus is a common condition that begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of your fingernail or toenail. As the fungal infection goes deeper, nail fungus may cause your nail to discolor, thicken and crumble at the edge. It can affect several nails. If your condition is mild and not bothering you, you may not need treatment. If your nail fungus is painful and has caused thickened nails, care steps and medications may help. But even if treatment is successful, nail fungus often comes back. Nail fungus is also called onychomycosis (on-ih-koh-my-KOH-sis). When fungus infects the areas between your toes and the skin of your feet, it's called athlete's foot (tinea pedis).
A rash is a change in the skin due to skin irritation. Most rashes go away on their own or require only minor treatment. Some rashes may need medical attention. Some rash symptoms are redness, itching, bumps, redness, and swelling. Some causes of rashes are allergic reactions; reactions to medications; plants such as poison ivy; or irritation due to jewelry, chemicals, or makeup. Rashes are also sometimes symptoms of another condition, as with impetigo or scabies. Treatments vary based on the cause, but many can be treated with medications.
This small flap of flesh-colored or slightly darker tissue hangs off your skin by a stalk. They’re usually found on the neck, chest, back, armpits, under the breasts, or in the groin area. Skin tags appear most often on women and elderly people. They aren’t dangerous and usually don’t cause pain unless they become irritated when clothing or nearby skin rubs against them. A dermatologist can cut, freeze, or burn them off.
A staph infection is caused by a Staphylococcus (or “staph”) bacteria. The infection often begins with a little cut, which gets infected with bacteria. This can look like honey-yellow crusting on the skin. These staph infections range from a simple boil to antibiotic-resistant infections to flesh-eating infections. The difference between all these is the strength of the infection, how deep it goes, how fast it spreads, and how treatable it is with antibiotics.
One type of staph infection that involves skin is called cellulitis and affects the skin’s deeper layers. It is treatable with antibiotics. This type of infection is very common in the general population – and more common and more severe in people with weak immune systems. People who have diabetes or weakened immunity are particularly prone to developing cellulitis.